Colours come in hues, tones, shades and tints. How they are created is different for digital and print colours. To make sure your digital devices and printer show exactly the colour you choose, they are represented with colour codes.
The basics
Let’s start with the basic terms. If I asked you about your favourite colour, chances are you would say blue or red or yellow. These very basic colours are called hues. Every hue has an entire range of colours. For example, blue comes in light blue, dove grey or navy. On Canva’s Color Wheel you can pick the hue in the big circle and the specific colour in the slim outer circle.
We create shades by adding black to a colour. Tints are the colour plus pure white and tones are a mix of a specific colour and grey. Online tools, like the Tint and Shade Generator, can do this automatically for you. On the picture below you see what the result looks like. The first square in the row is the original colour I put into the generator.
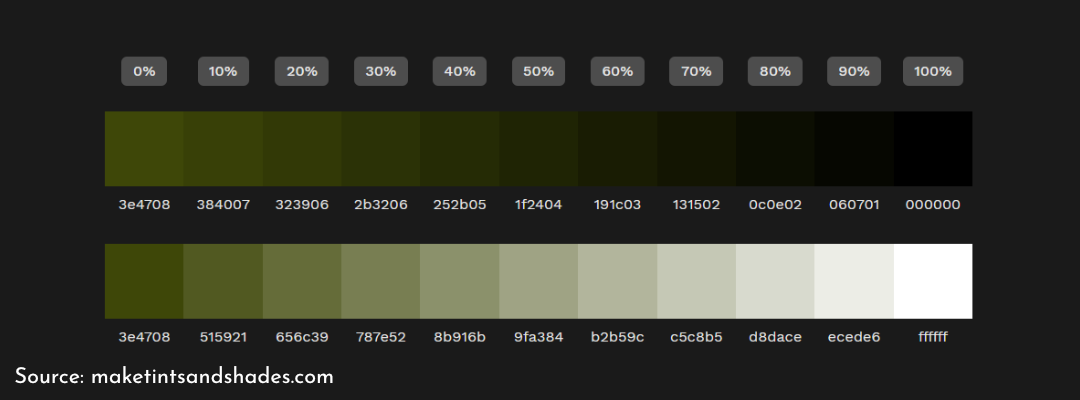
The generator I used to create different tints and shades adds black and white in increments of 10%. There are more tints and shades in between thought. So how do displays and printers know exactly which colour to show you? They use codes, meaning every colour is expressed through a series of letters and/or numbers.
Colour codes
Electronic devices create colours by shining light at you. Screens consist of tiny pixels in different colours that together form the images and text you see. Which colour each pixel has, depends on how much of each primary colour is emitted. The primary colours in the digital world are red, green and blue.
So every colour is broken down into how much red, green and blue is present. The result is the colour code specific for each shade, tint and tone. The two most important colour codes used for digital design are the HEX code and the RGB code.
HEX code
The HEX code consists of six numbers or letters and expresses how intense the red, green and blue in the specific colour is. The lowest intensity is 00 and the highest is FF. White, for example has all three colours at the highest intensity, so the HEX code for white is #FFFFFF. Black is the opposite: #000000.
Pure red has the highest intensity of red and no green or blue, which makes its HEX code #FF0000. And so on. You can easily recognize HEX codes by the # before the numbers and letters. Since it’s widely used on websites and graphic design programs, HEX is one of the easiest ways to make sure you always have the same colour where you want it to, for example your brand colour. Just copy and paste the HEX codes for all of your colours and re-use them any time you need to.
RGB and RGBa
The RGB code works like the HEX code, except it only consists of numbers. Three numbers express how much red, green and blue is present to create a specific colour. The numbers range from 0 to 255. So red has tge RGB code 255, 0, 0. RGBa adds the alpha channel to colours. This is an additional number that expresses how transparent the colour is.
You do not need to memorize colours and colour codes. Just know that your computer and phone and any other digital device that shows you different colours uses these codes to display them. All you need to know is where to get them, from example by using colour wheels, and how to copy and paste them.
Print: CMYK
The digital colour models above are called additive colour models because they add light shining at different intensities to create a new colour. In printing, the colour model is subtractive because the inks used cover up the light that would normally be reflected back from a light or white surface, like printing paper, for example.
The ink colours used are cyan, magenta, yellow and key, which is usually black. Cyan and yellow combined create green, cyan and magenta create blue and yellow and magenta create red. That’s how these different inks are used for the primary colours which can then be combined in all kinds of strengths to form any colour needed.
What you need to know
If you work with a graphic program, you might want to check your settings. Some programs created for non-designers, like Canva, will automatically change the colours of your document to optimize them for print if you choose the right file type when you export it. For example, Canva allows you to choose pdf for print.
If you use a graphic design program created for professionals, like Affinity Designer, you want to choose or change the colour settings of your document to whichever model you need. RGB for files that stay digital and CMYK for print files.
Colours are very powerful. They can even influence how we feel. Knowing the basics about colours helps understanding how to use them to attract the perfect audience, clients, and fans for you.